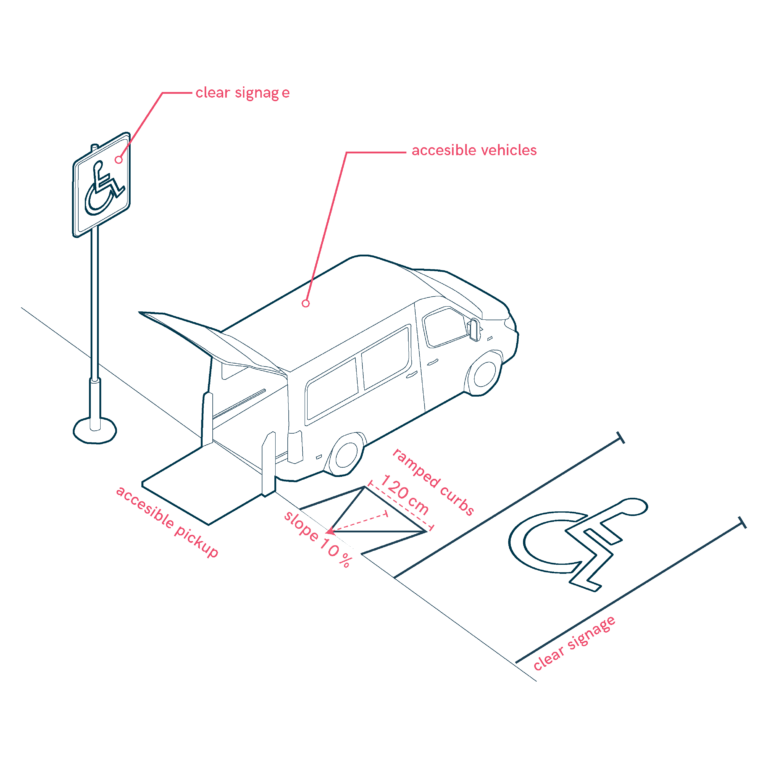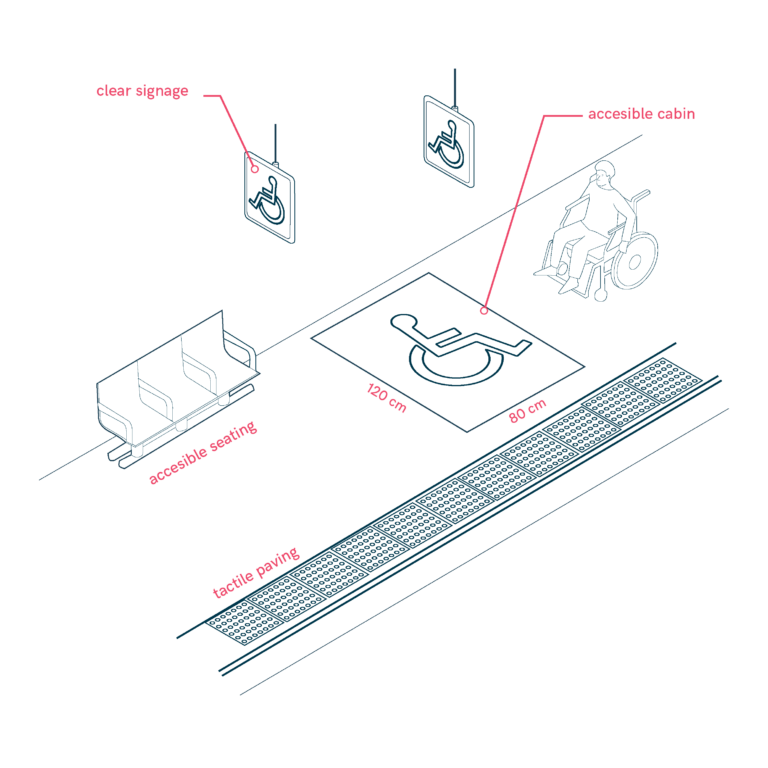
Low-education
Spectrum of abilities
People with lower educational levels or who have received education that differs from the standardized system of the territory they live in exhibit a variety of skills and needs depending on their experiences and contexts. While they may face limitations in accessing opportunities and resources, many develop practical knowledge and transversal social skills. The lack of formal education can affect social and cultural inclusion. However, many of these individuals create alternative cultures with significant value to society as a whole.
Accesibility and inclusion actions
To improve the inclusion of these individuals, it is essential to implement accessibility measures in both physical and digital spaces. In the physical environment, this includes simplifying bureaucratic processes and providing access to essential services without barriers. Additionally, to integrate their own realities, spaces must be inclusive of any user. In the digital environment, digital literacy, intuitive platform design, and the availability of accessible educational resources help reduce the digital divide and facilitate their participation in society.
Key beneficiary users
The proposed accessibility measures would benefit various profiles of people with lower educational levels or who have received education that differs from the standardized system in their environment. For example, older adults who, due to educational limitations, face difficulties understanding and using public services or accessing essential information. Also, workers in informal sectors who lack formal academic training struggle to access public services, education, or formal employment. Additionally, migrants who have been educated in different systems face barriers to fully integrating into society due to cultural and educational differences. These measures would enable these individuals to improve their quality of life, access essential services, and actively participate in the community.

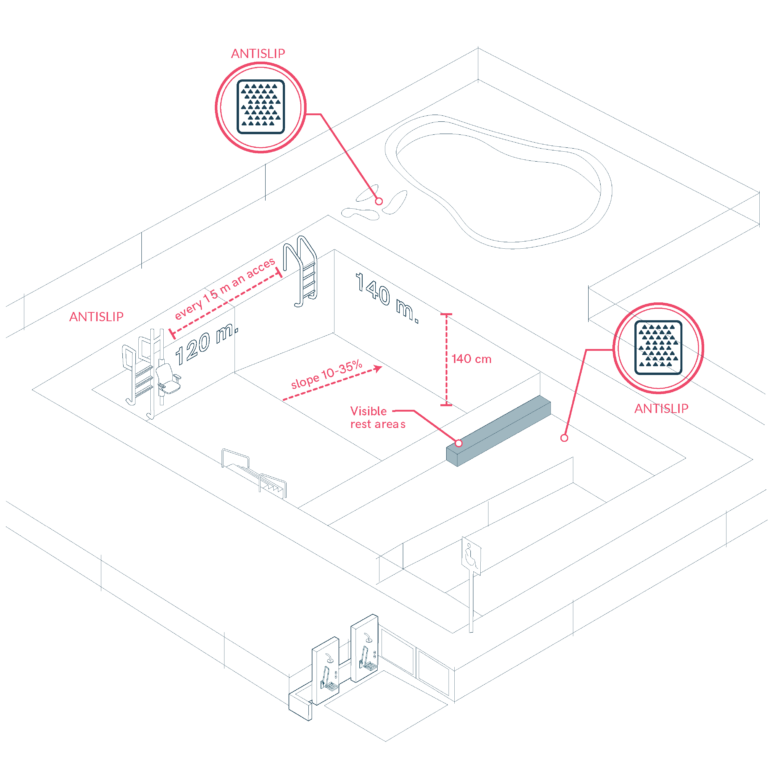
Accessibility in Swimming Pools
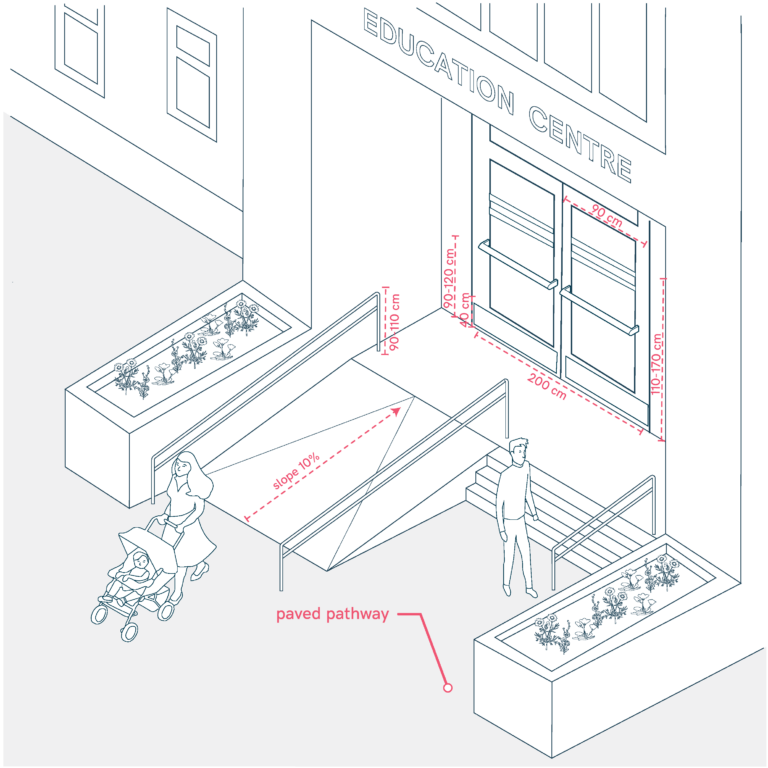
Accessible Entrance and Gates
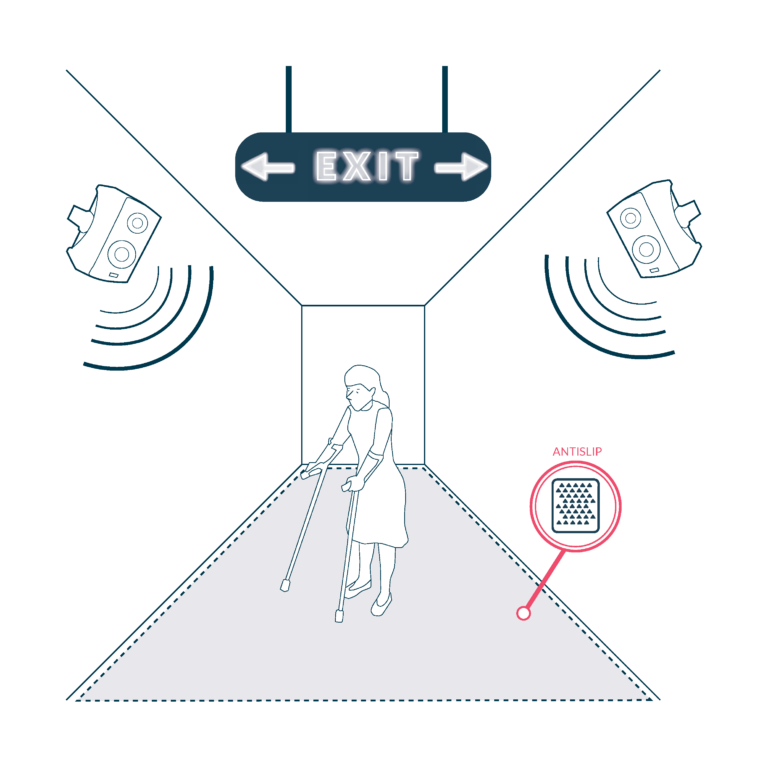
Accessible Gangways for Vessel Access
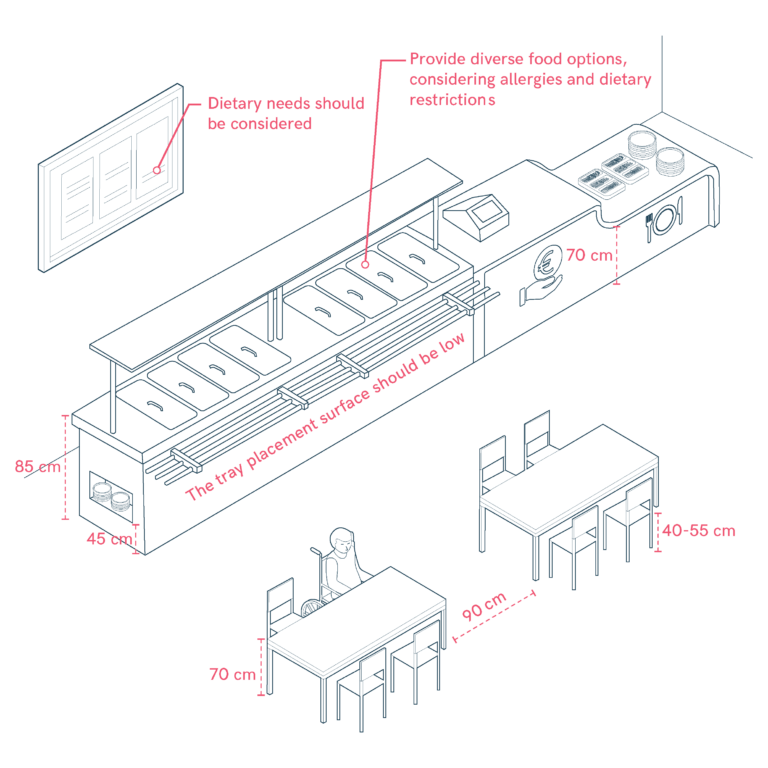
Accessible Lunch Counters and Tables
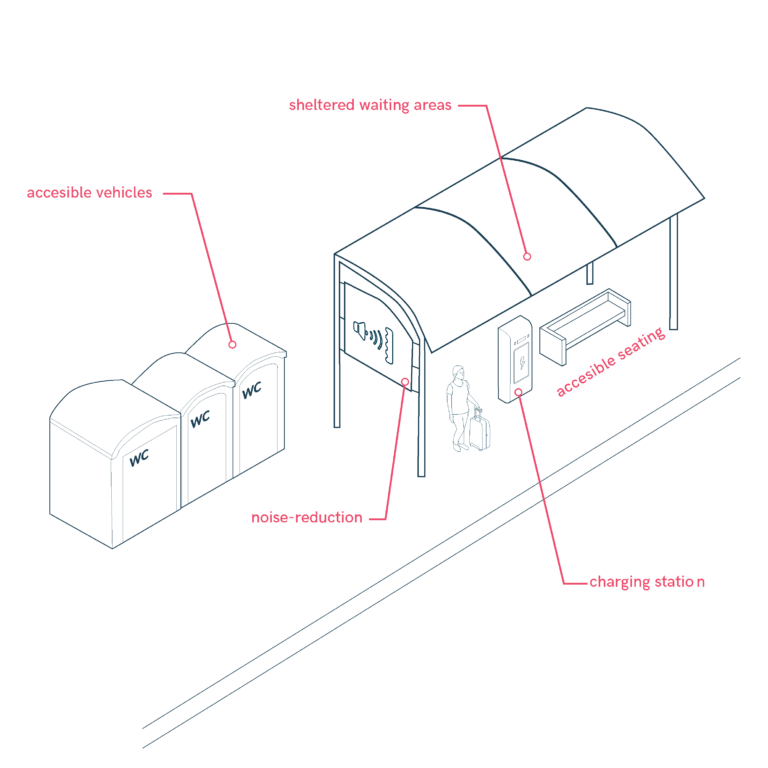
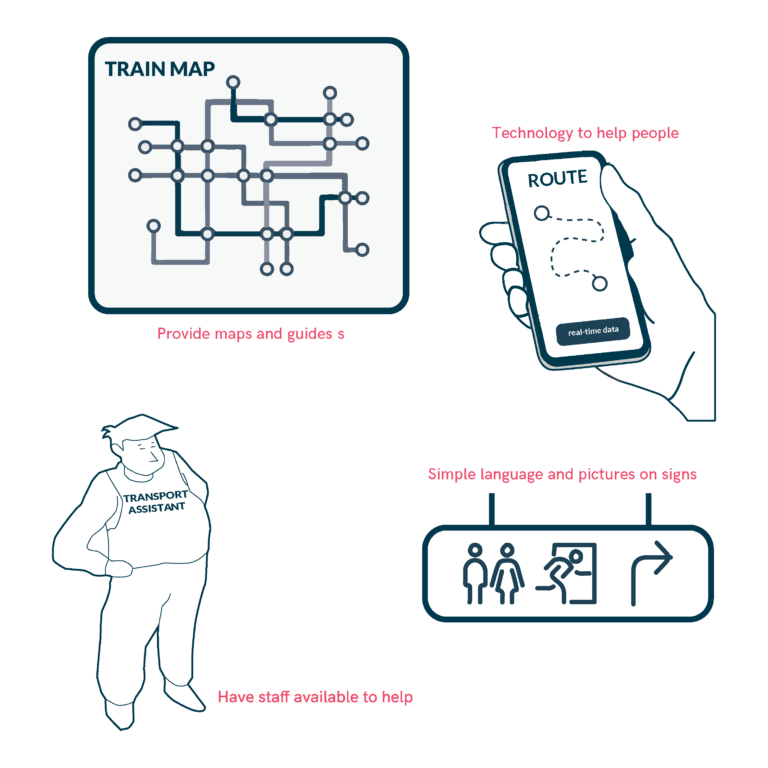
Accessible Waiting Areas and Station Facilities at Mobility Hubs
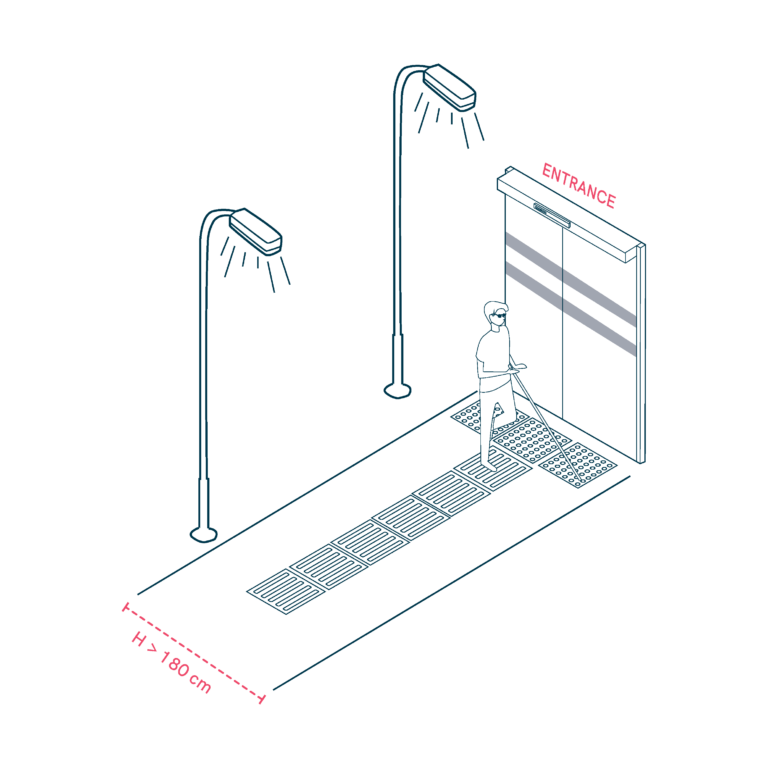
Around the Mobility Hub
Cells and Detention Spaces
Circulation Within Educational Centers
Cognitive-Friendly Design
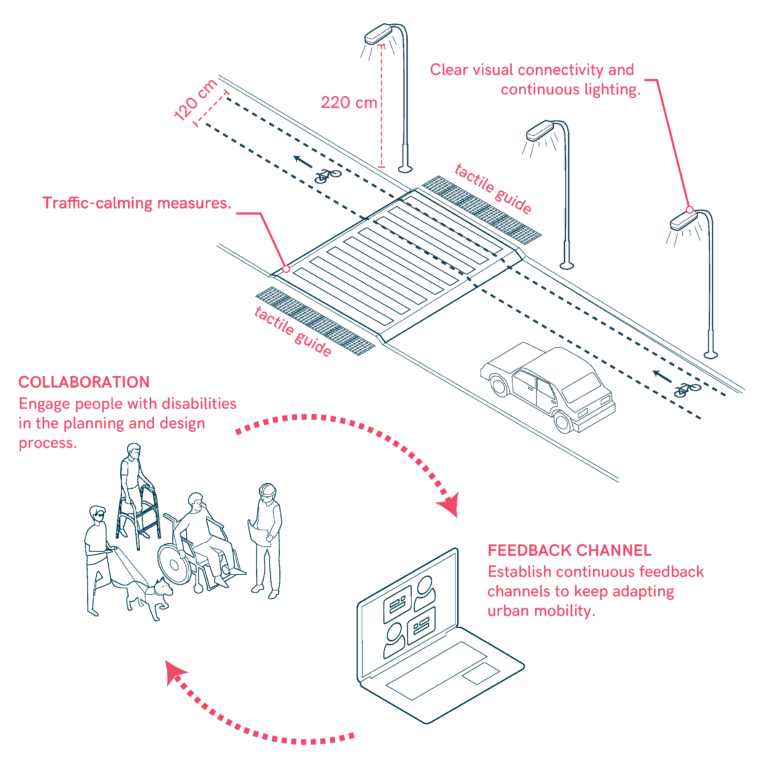
Community Engagement and Feedback
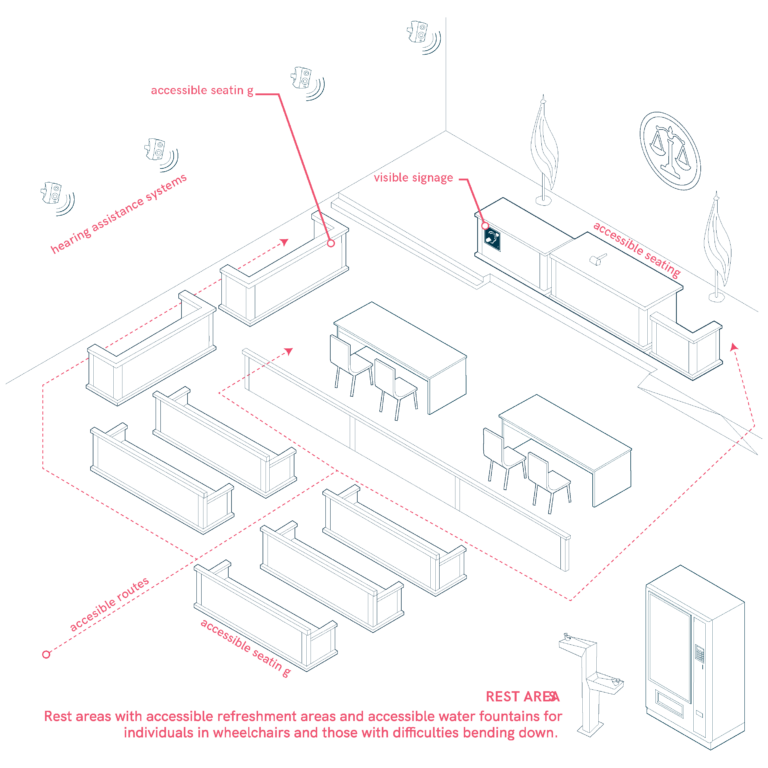
Courtrooms
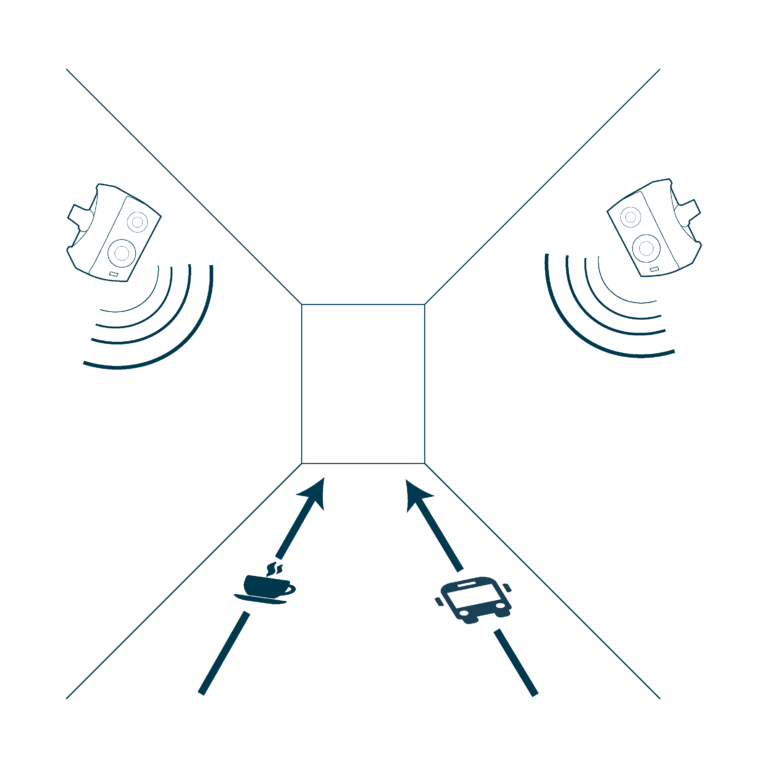
Create Safe Transitions Between Surfaces
Designing Hallways on Passenger Vessels
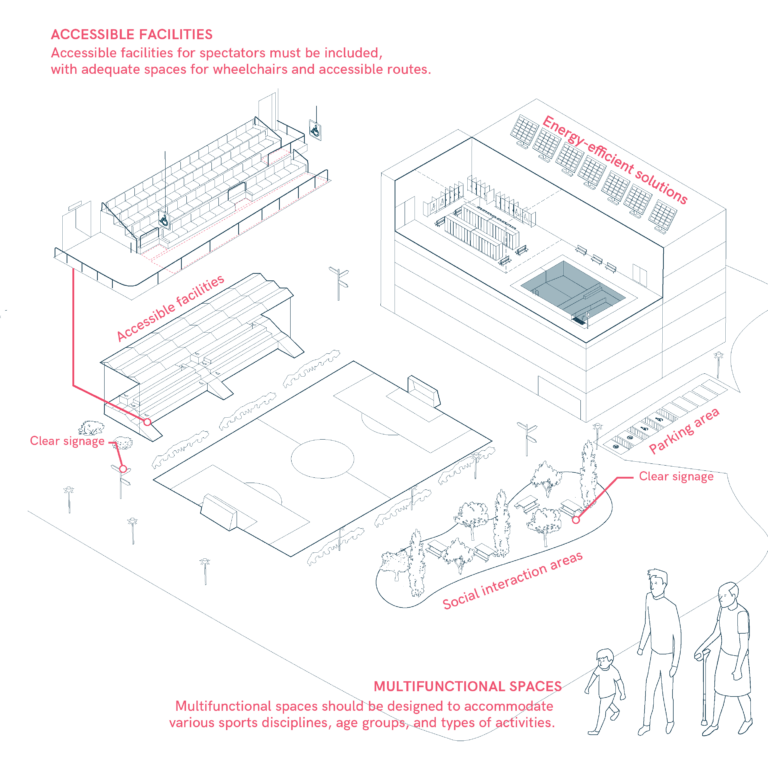
Designing Inclusive Sports Areas
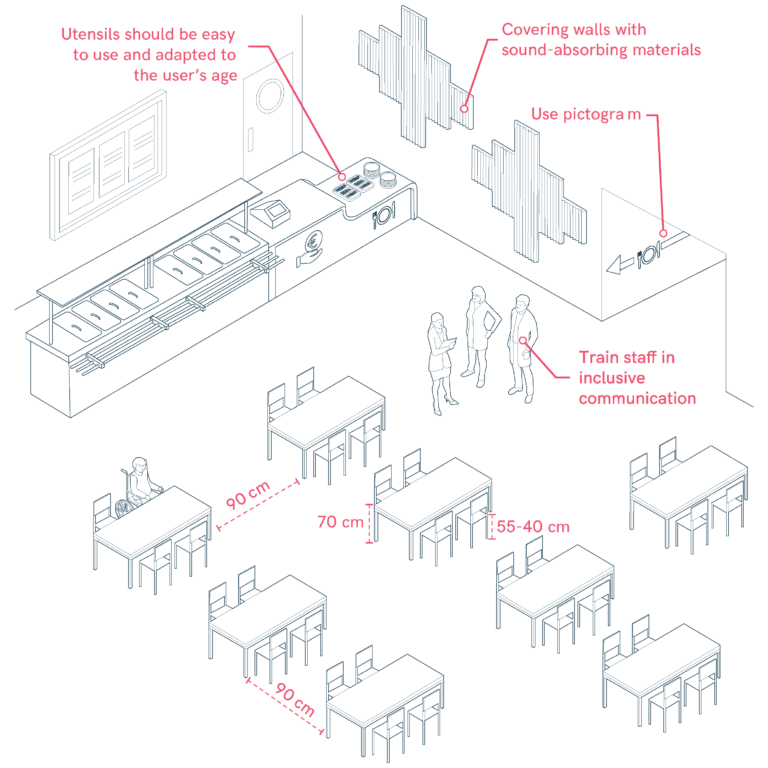
Dining Room in Schools
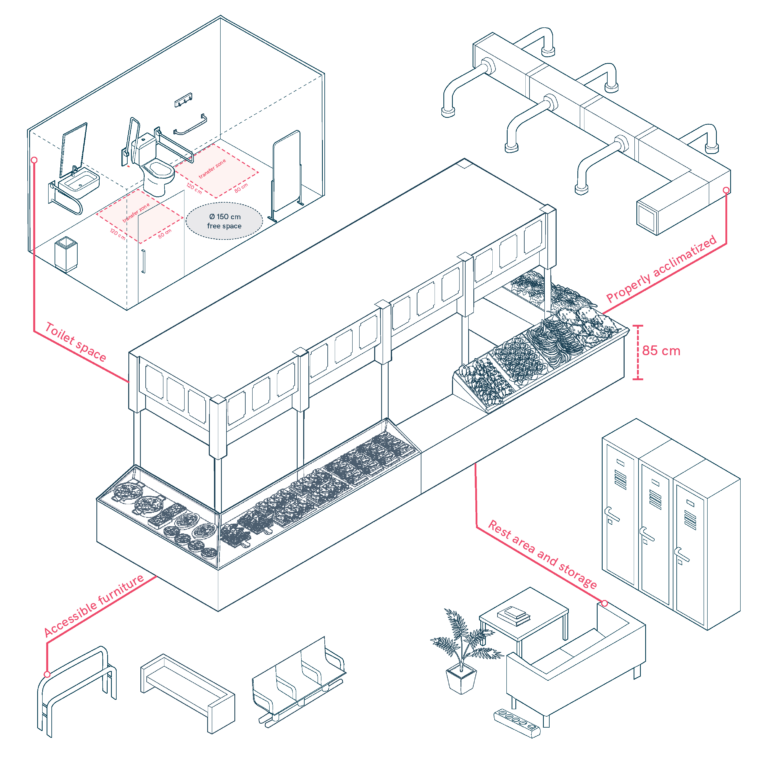
Diverse furniture and Market Stalls
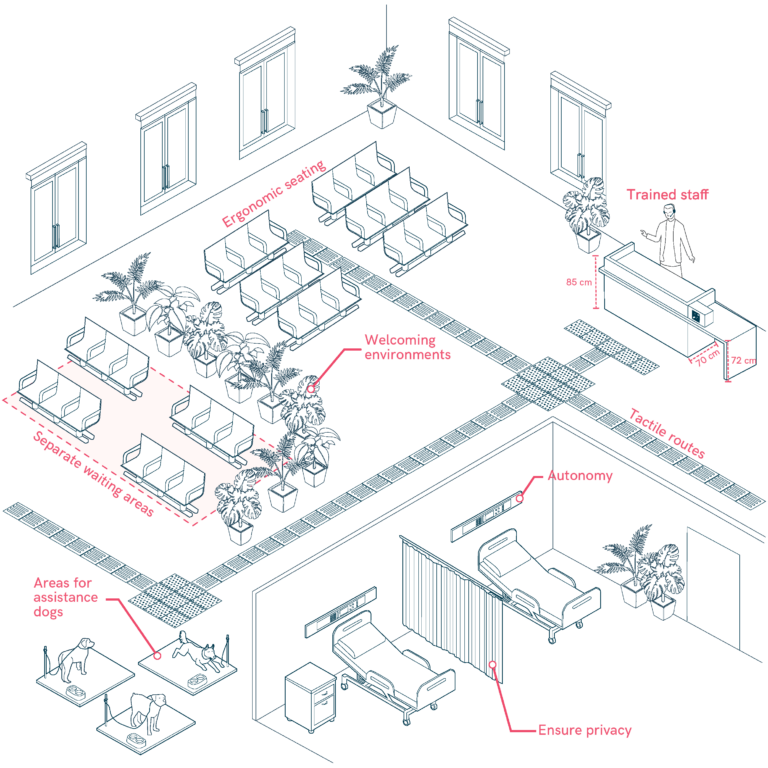
Emotional Accessibility
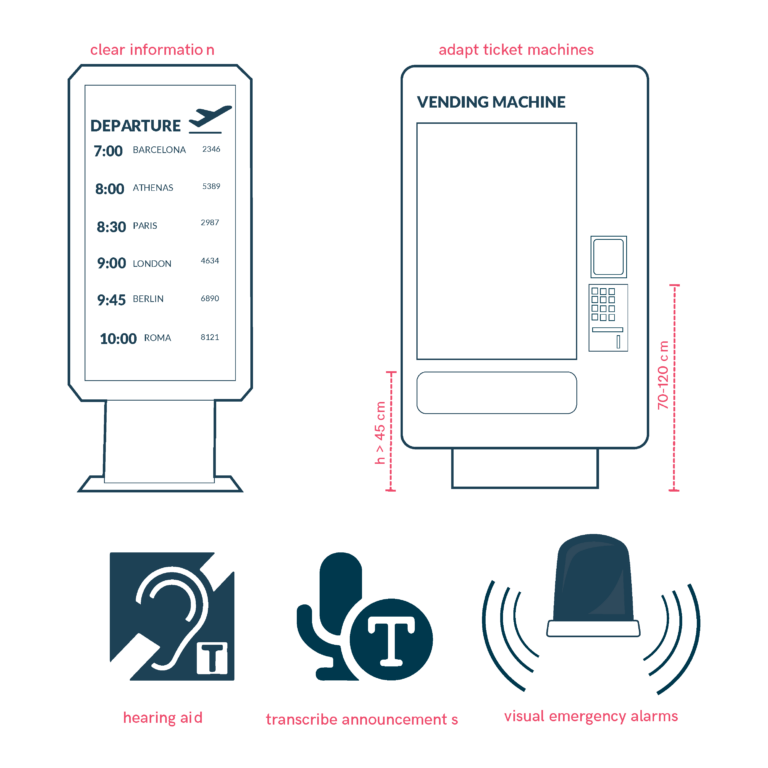
Ensuring Accessibility at Airports
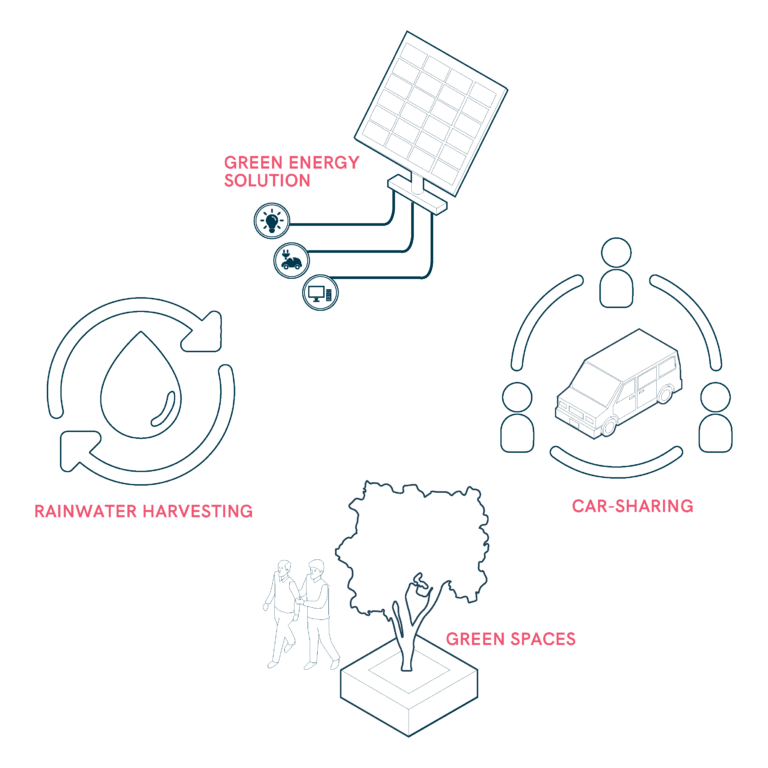
Environmental Sustainability at Mobility Hubs
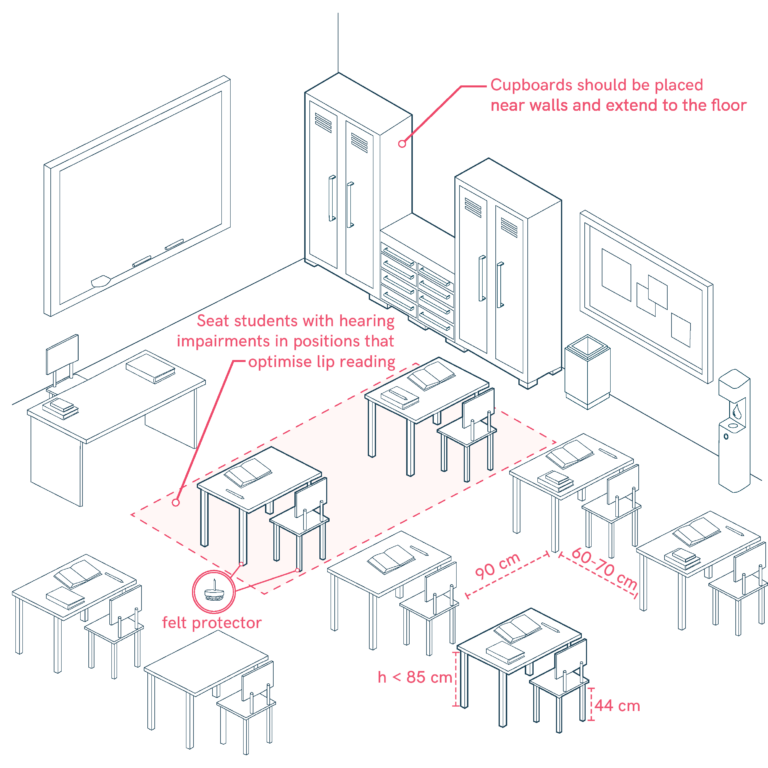
Ergonomic Furniture for classrooms
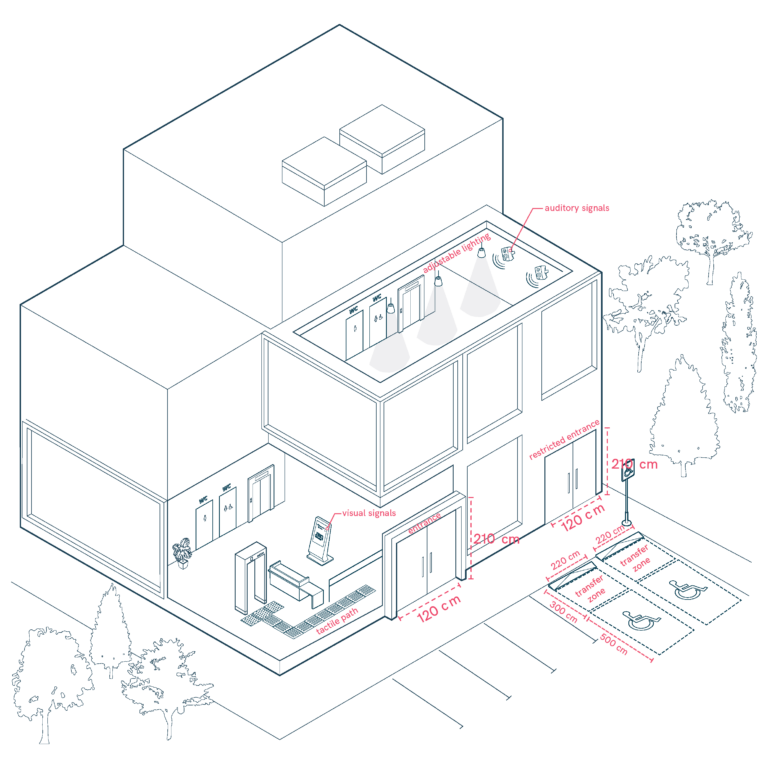
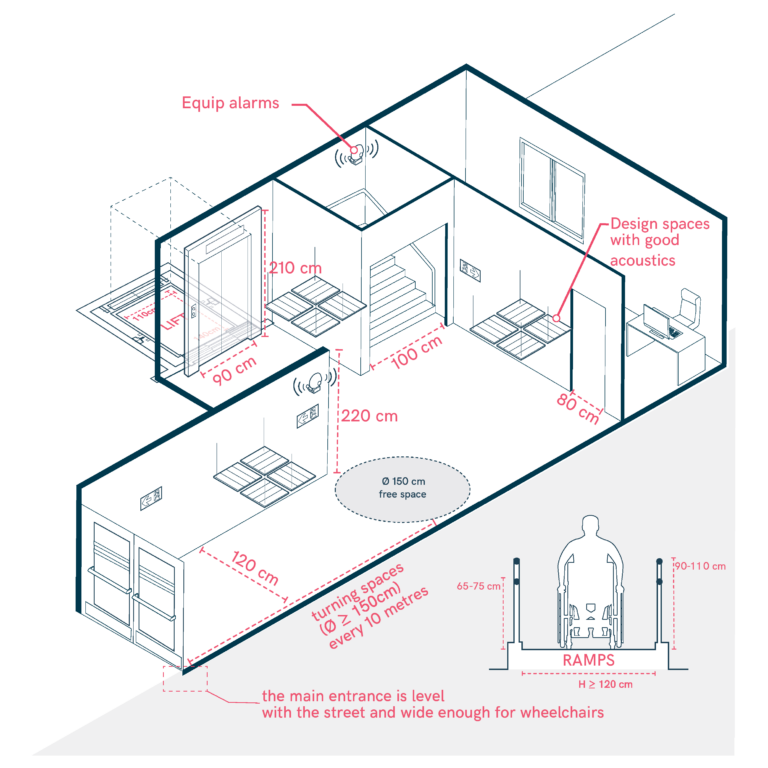
General Aspects of State Buildings
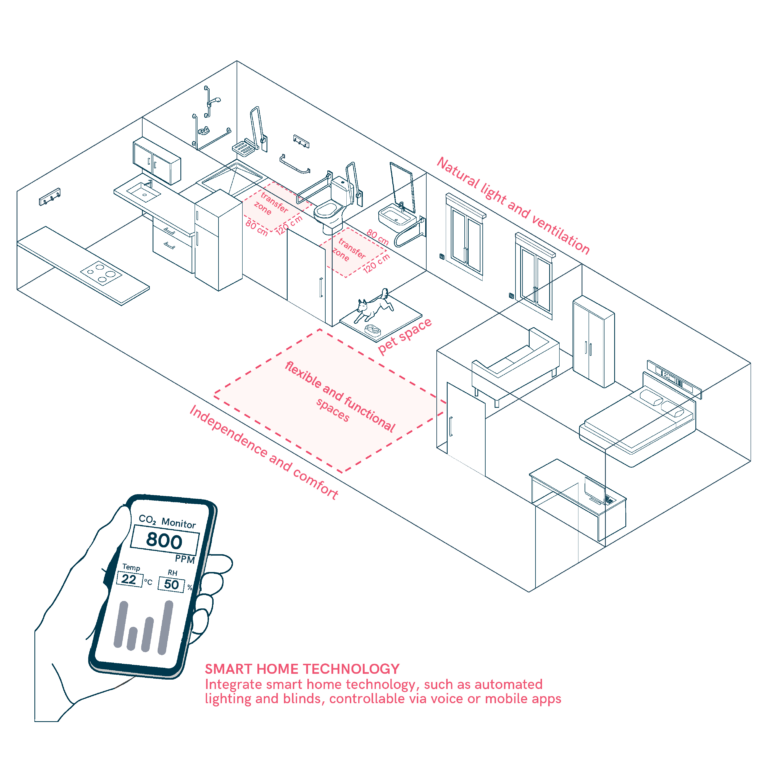
Home
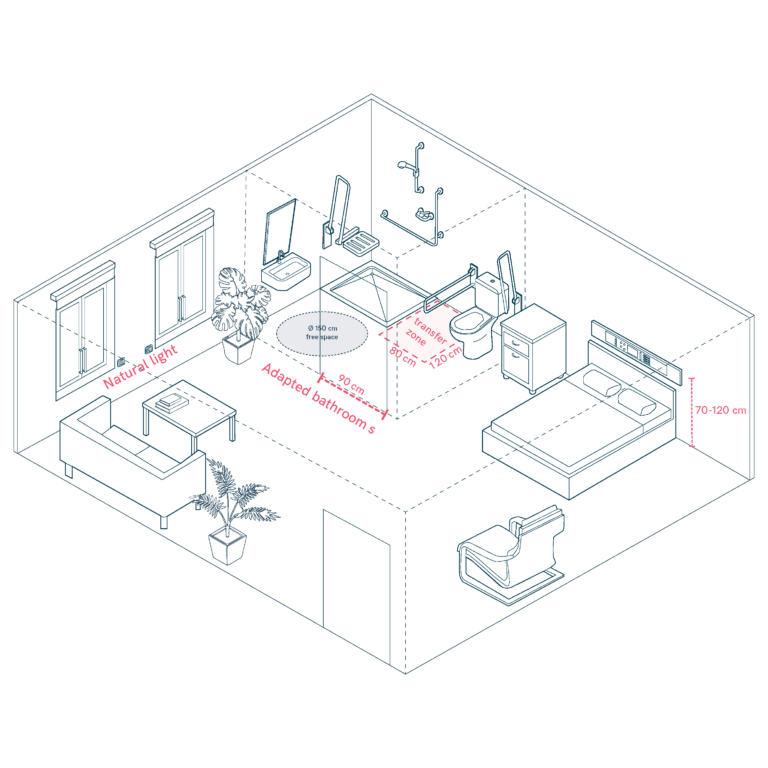
Humanised Patient Rooms
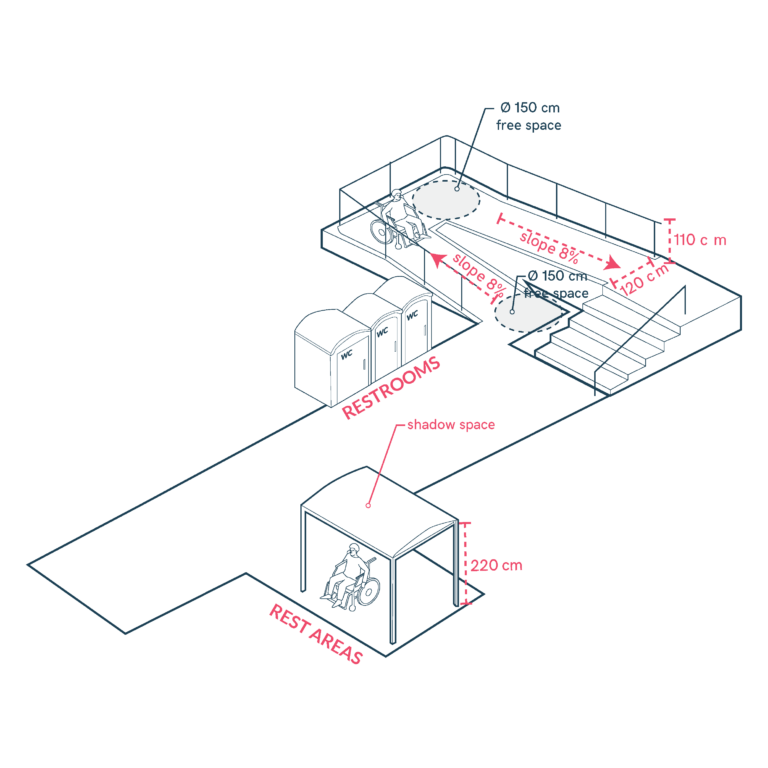
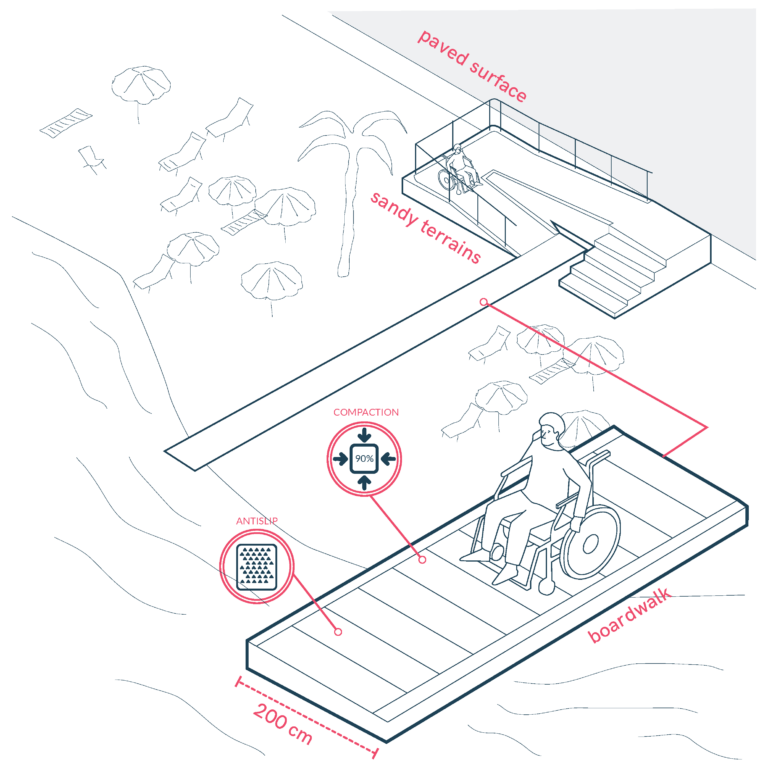
Inclusive Beach Access for All
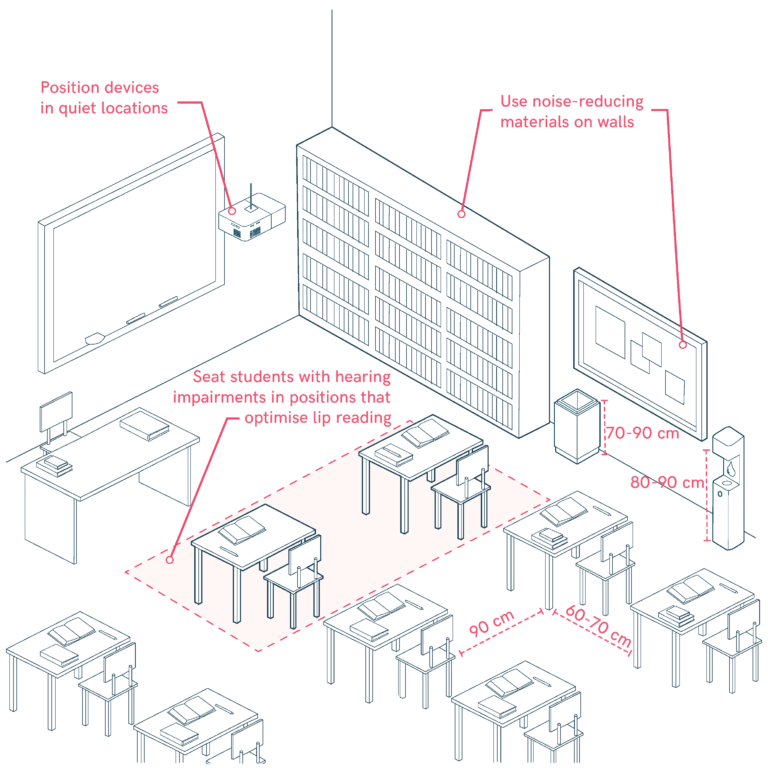
Inclusive Classroom Design
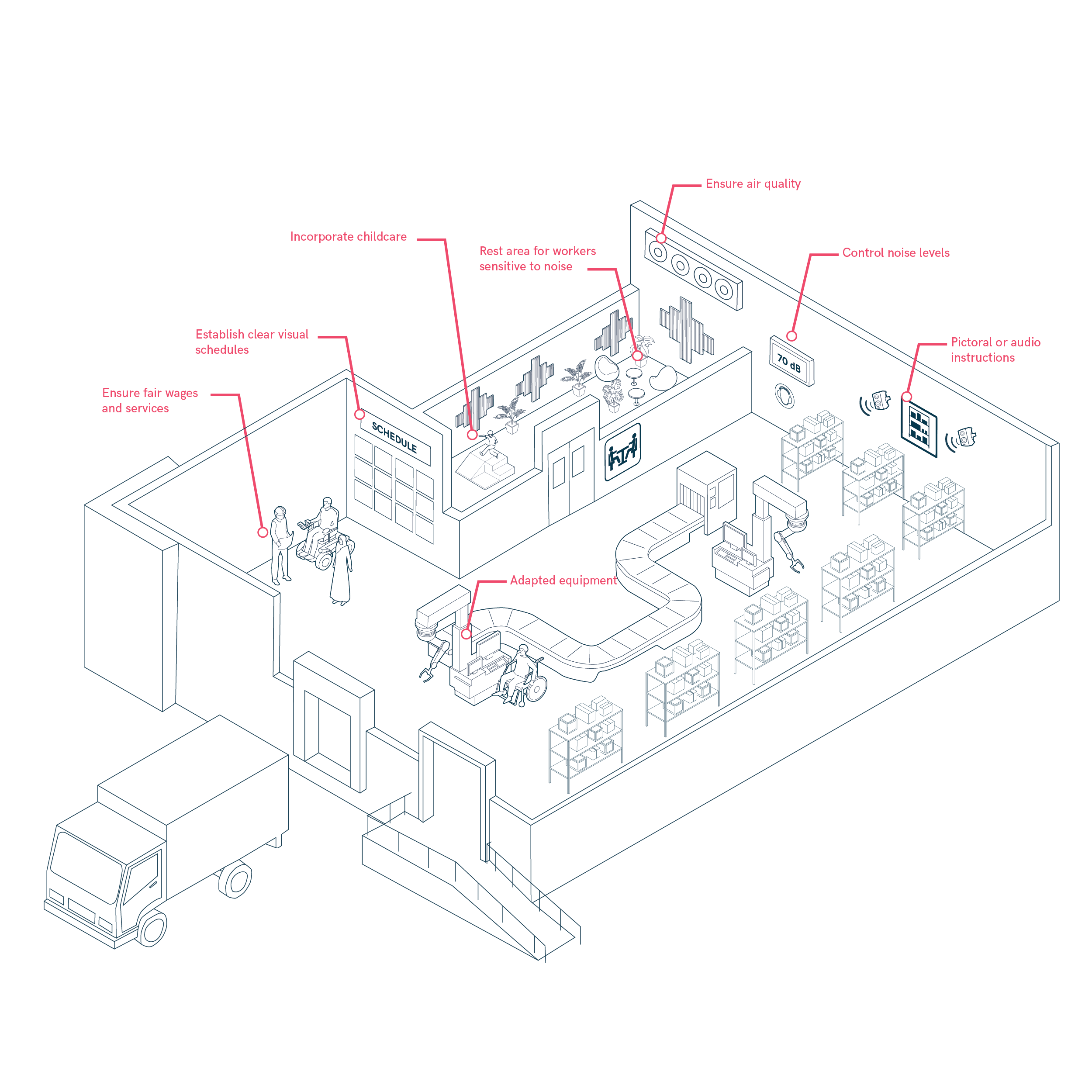
Industrial spaces
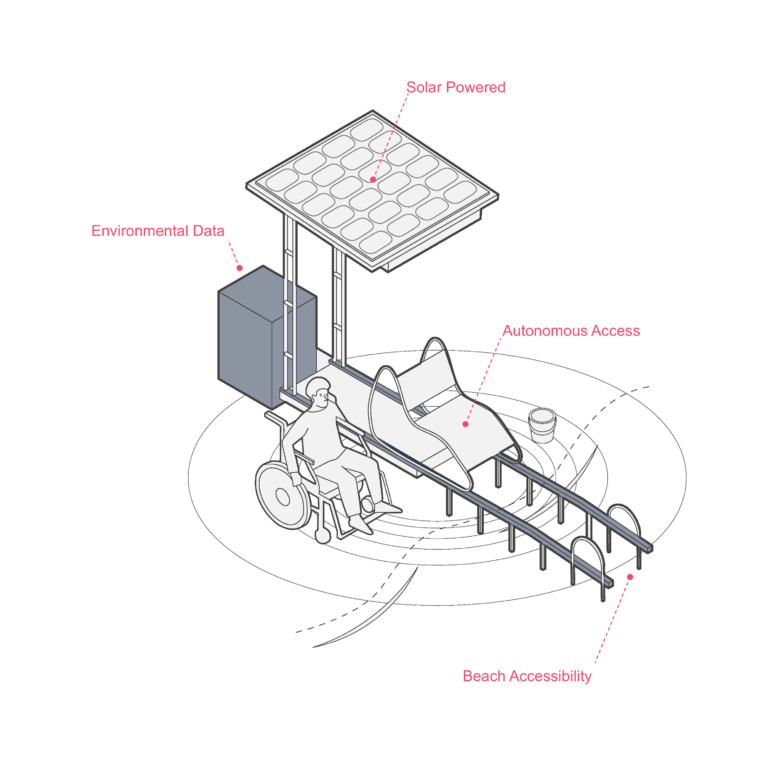
Innovative Beach Access Solutions (e.g., iSEATRAC)
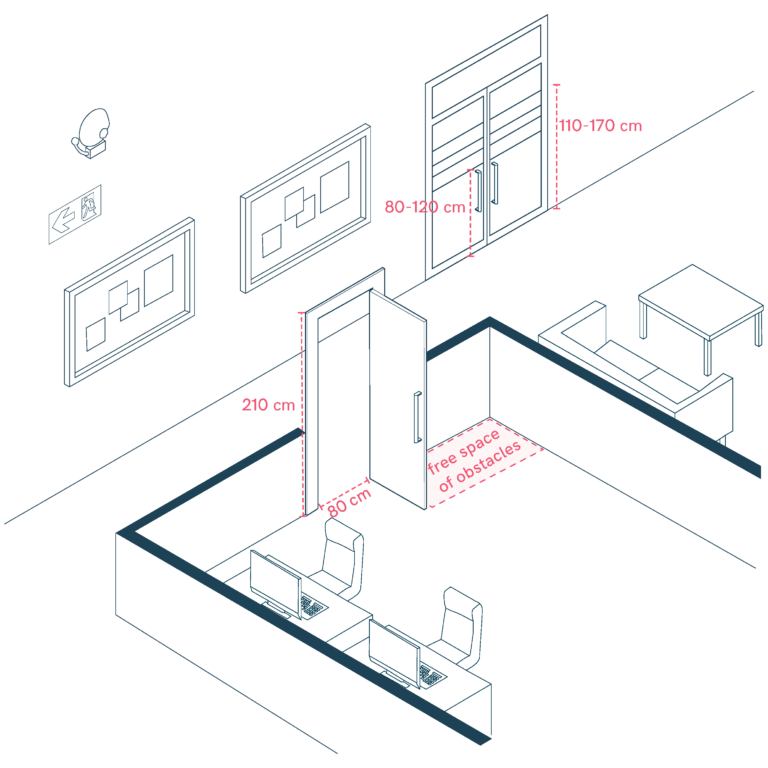
Interior Doors
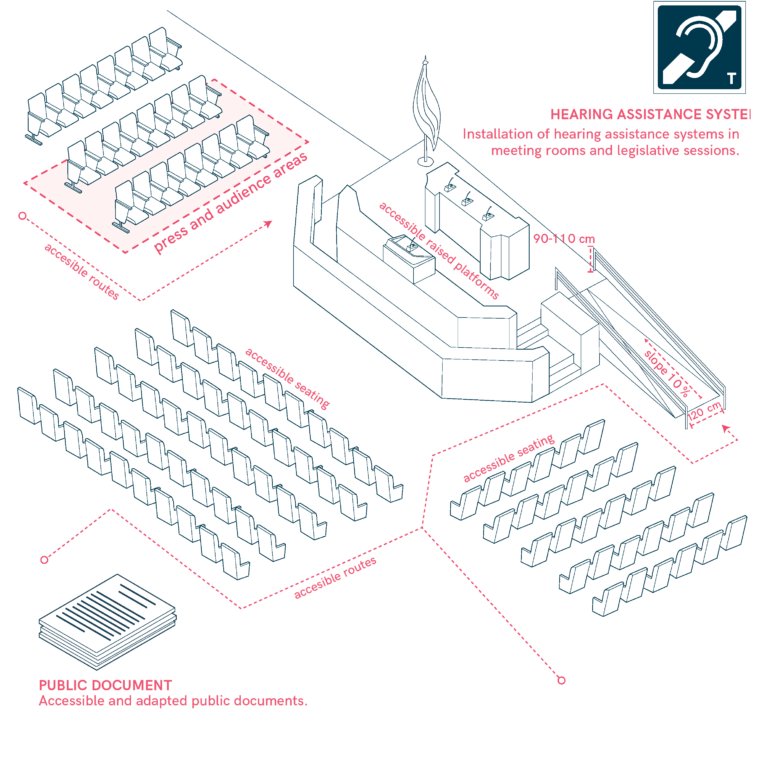
Legislative Buildings
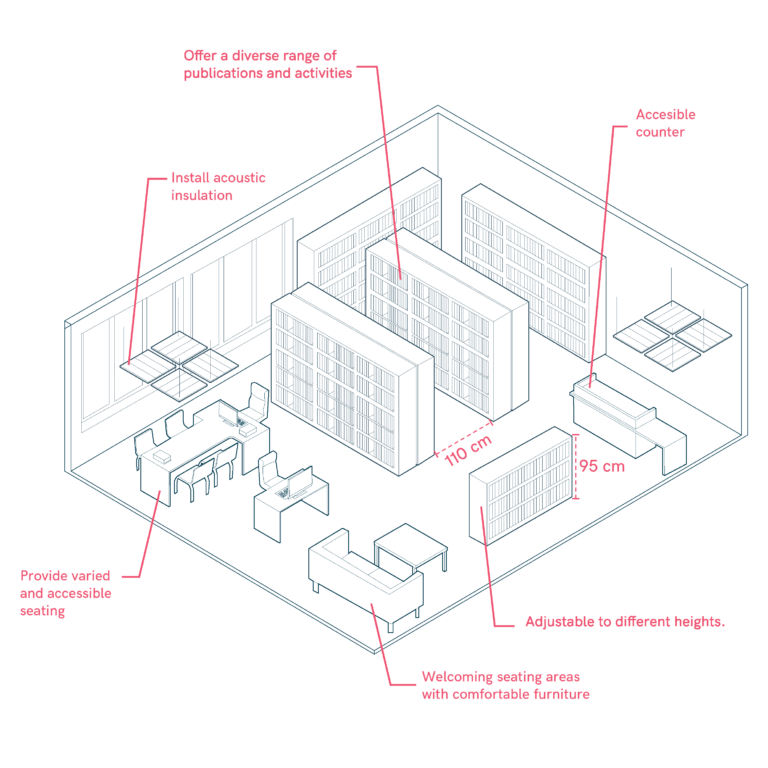
Libraries
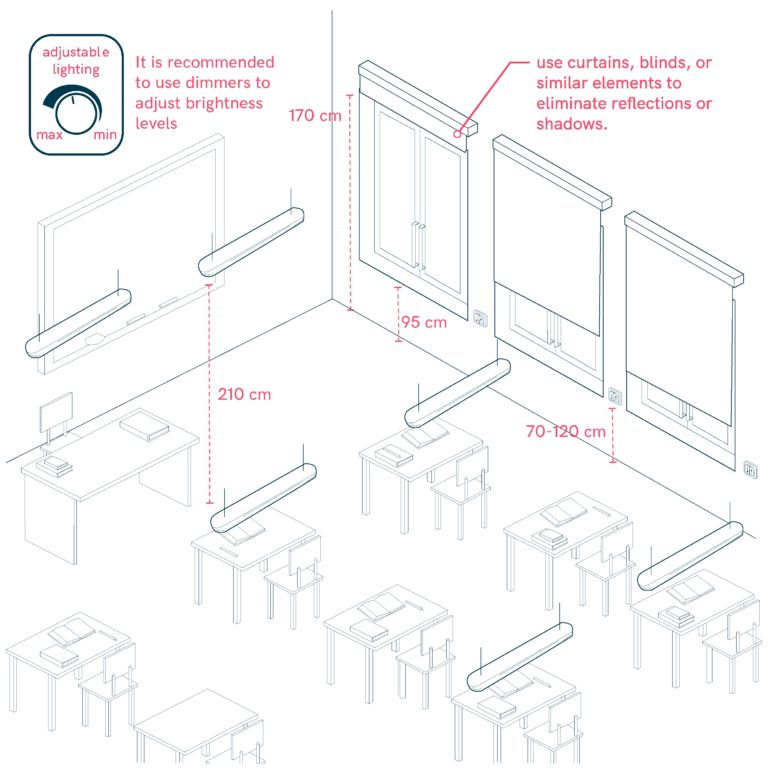
Lighting Considerations in Educative Centers
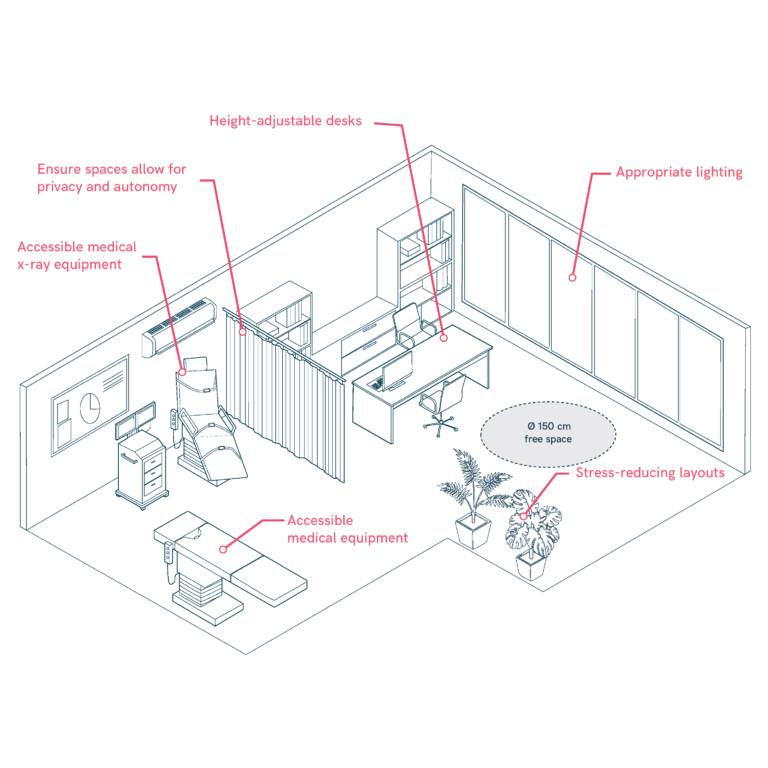
Medical Consultations
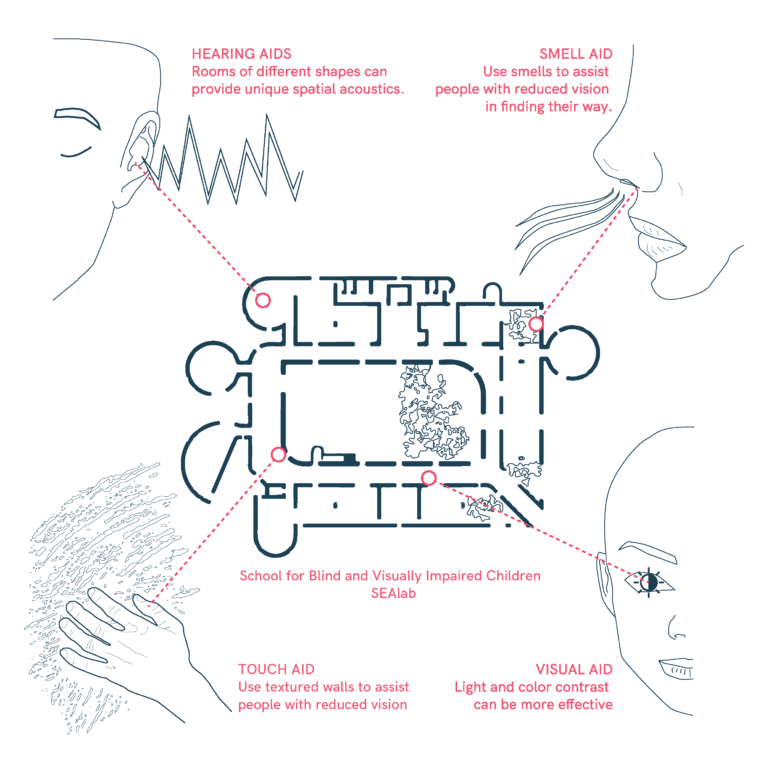
Multisensory Navigation and Spatial Orientation
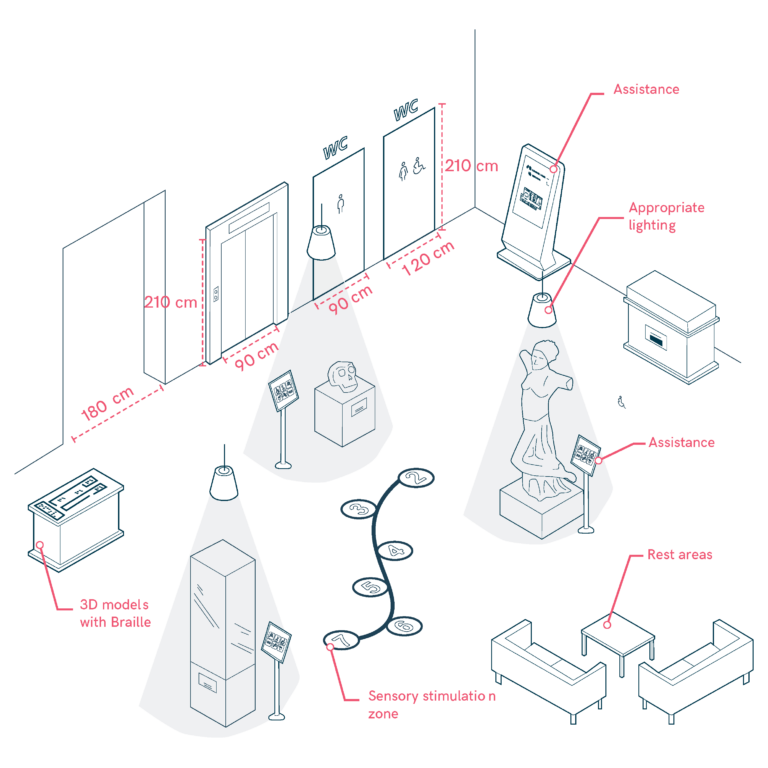
Museums and Heritage Sites
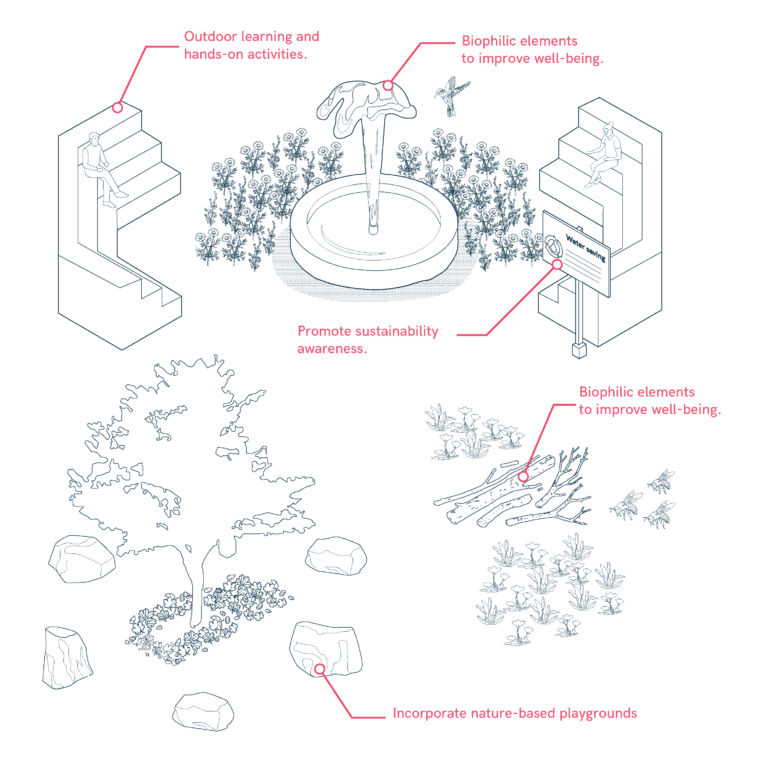
Natural Elements and Outdoor Learning
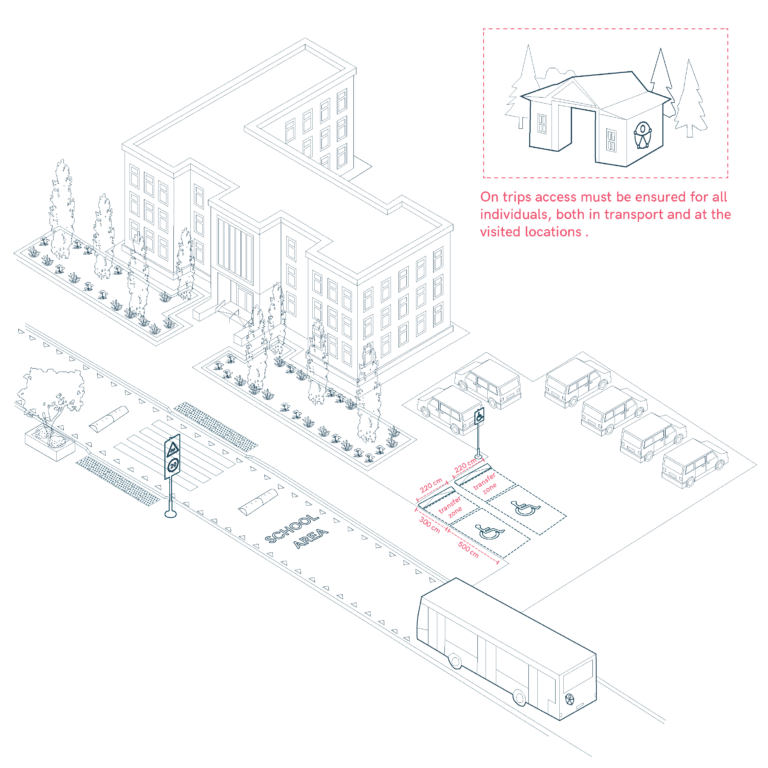
Parking and School Bus Accessibility
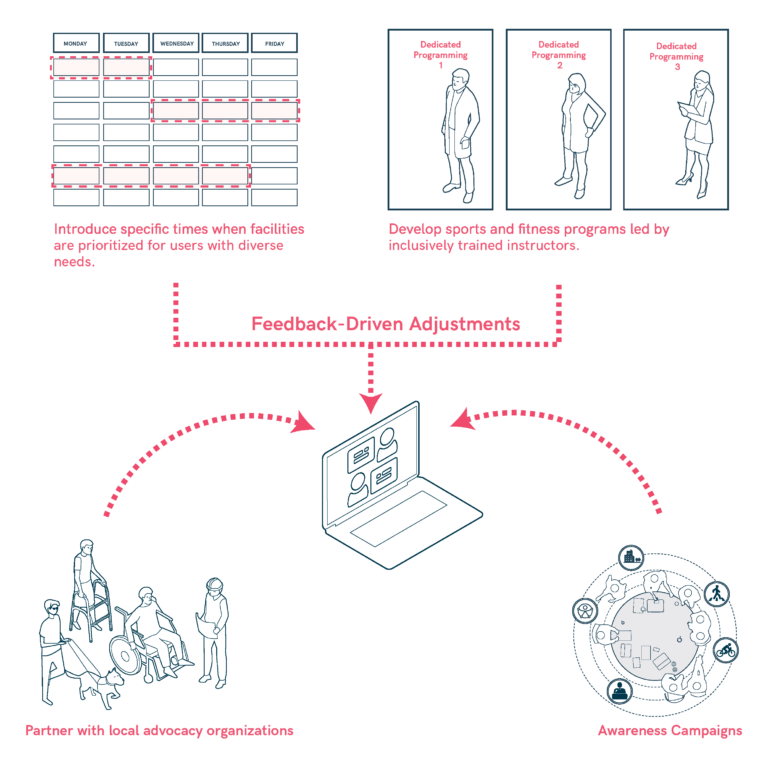
Programming and Pilot Initiatives
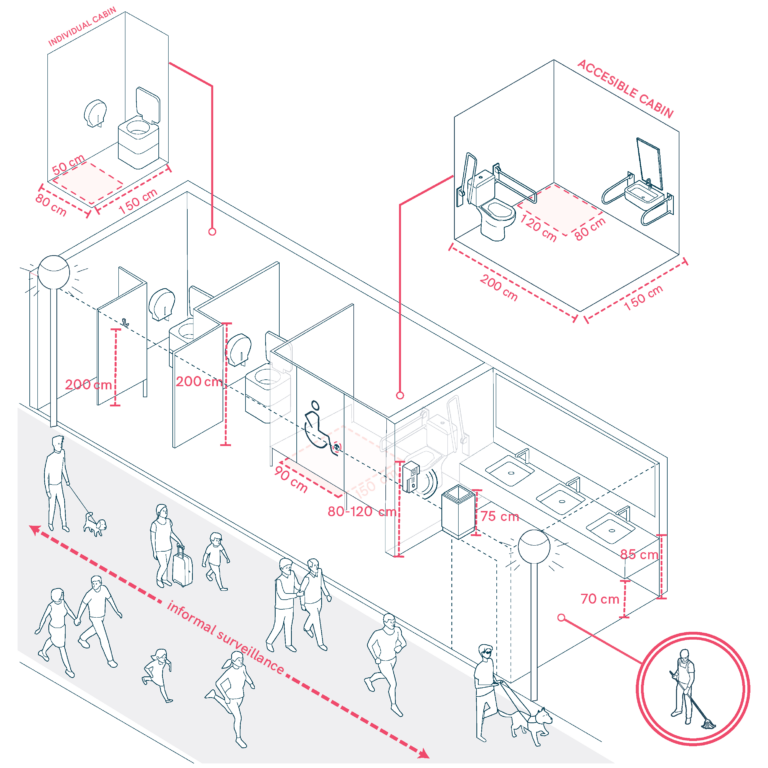
Restrooms in Mobility Hubs
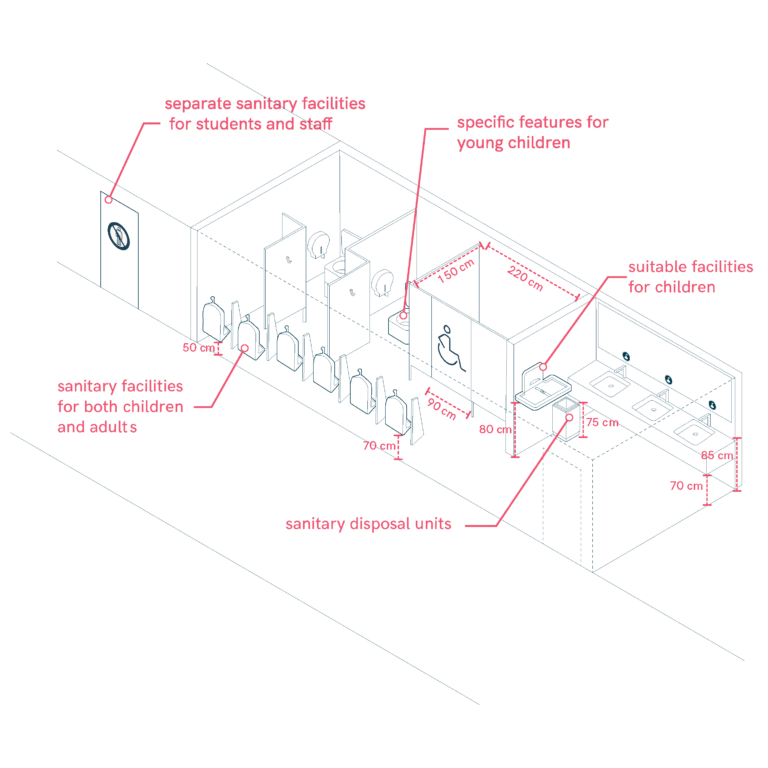
Sanitary Facilities and Restrooms
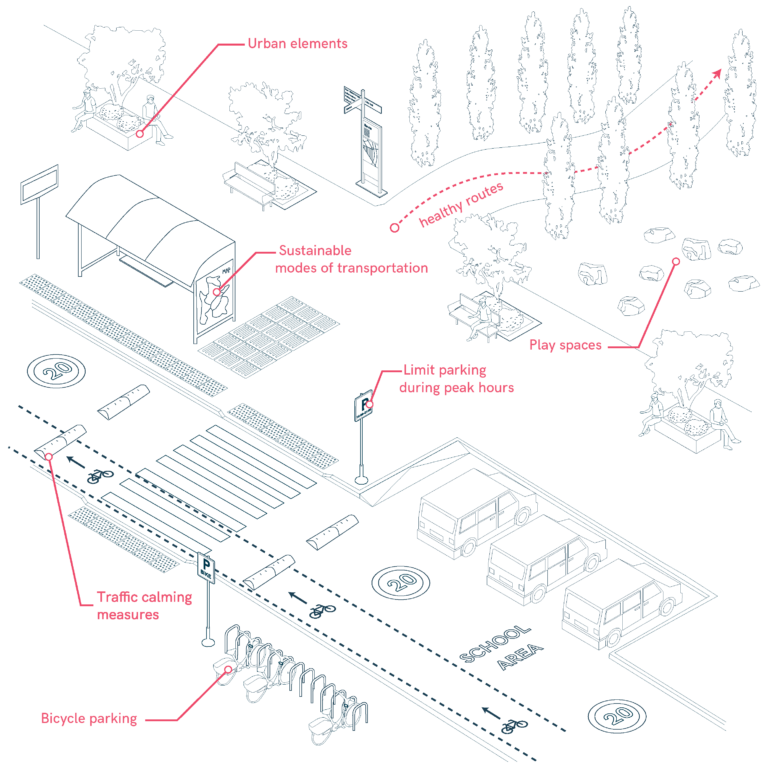
School Pathways
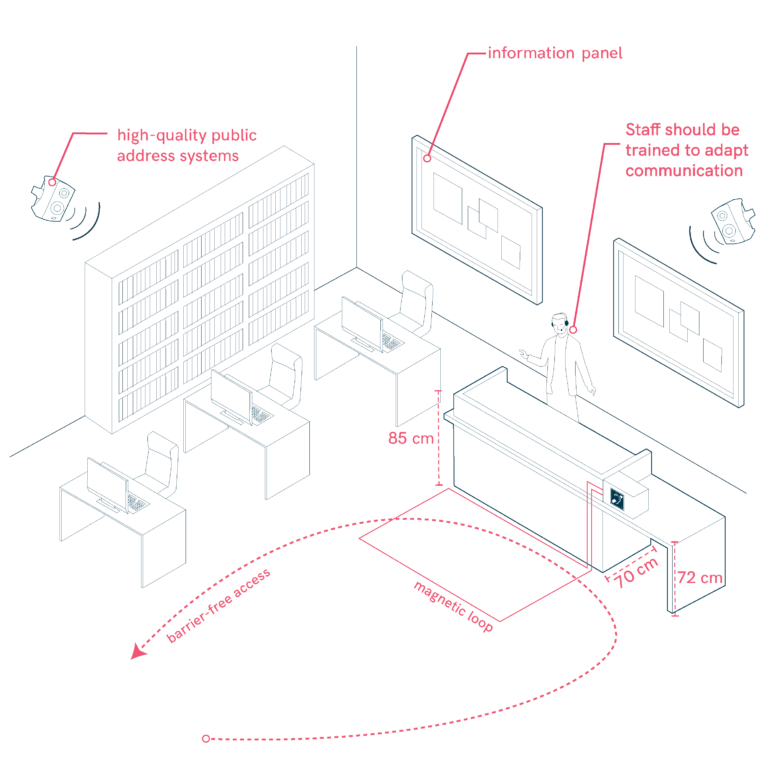
Secretary’s Office Accessibility
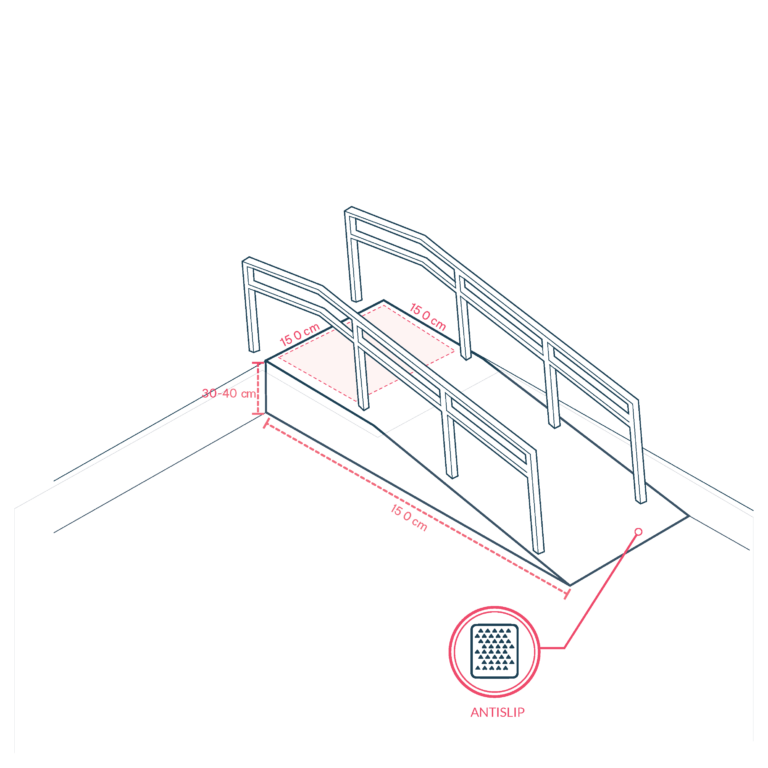
Slopes in swimming pools
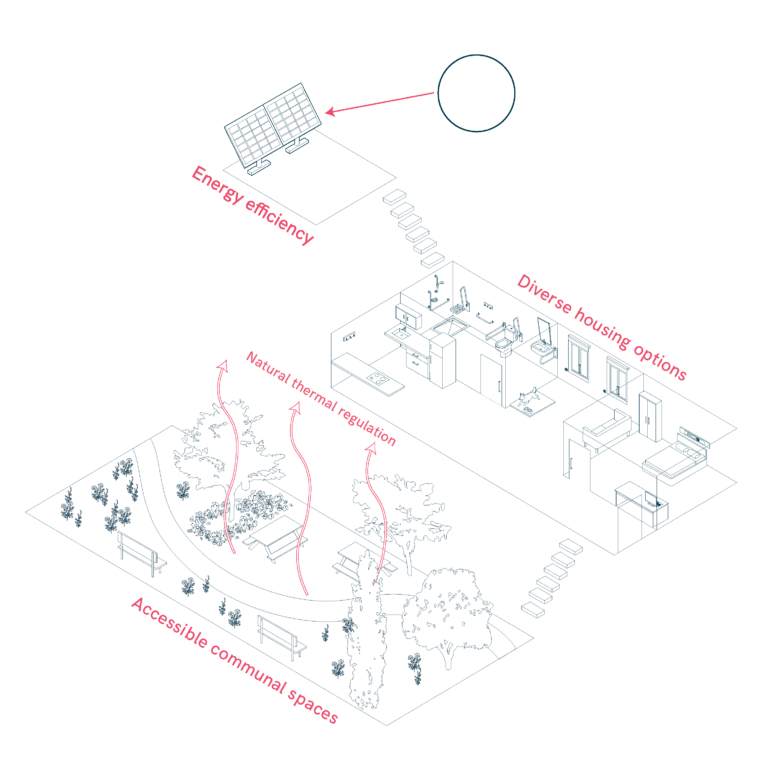
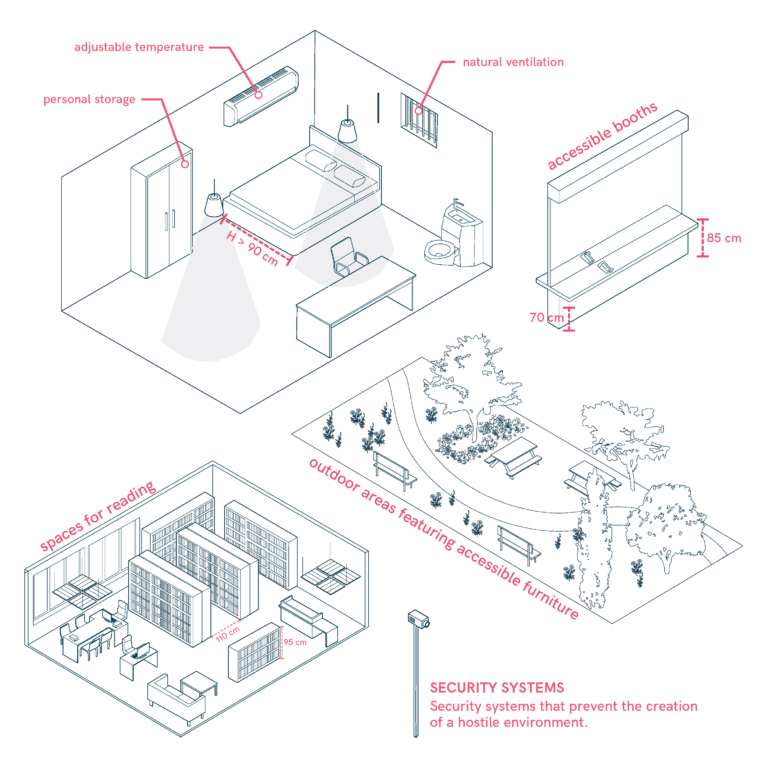
Social and Community Housing
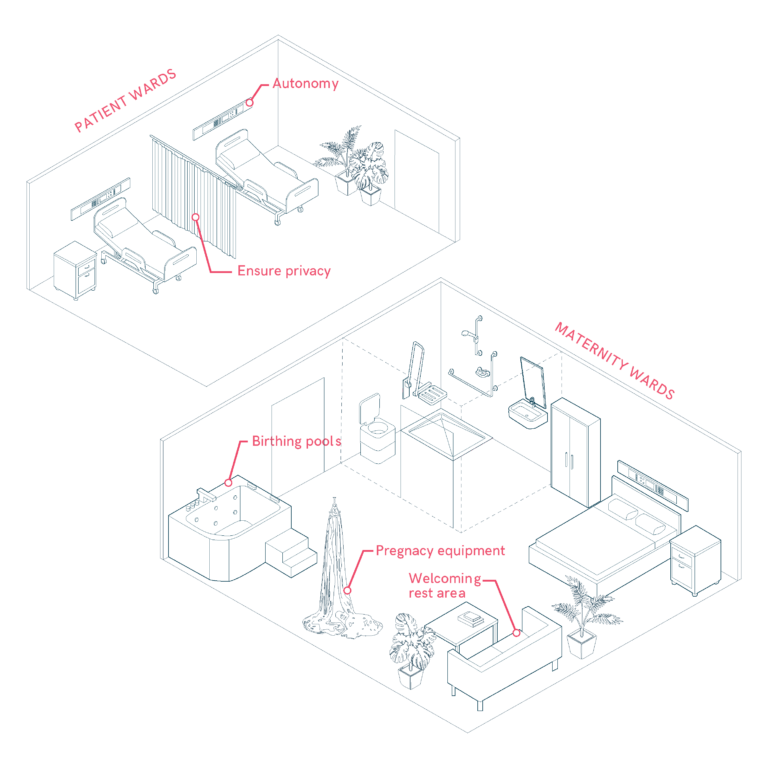
Specialist Areas and Medical Equipment

Sustainable and Resilient School Streets
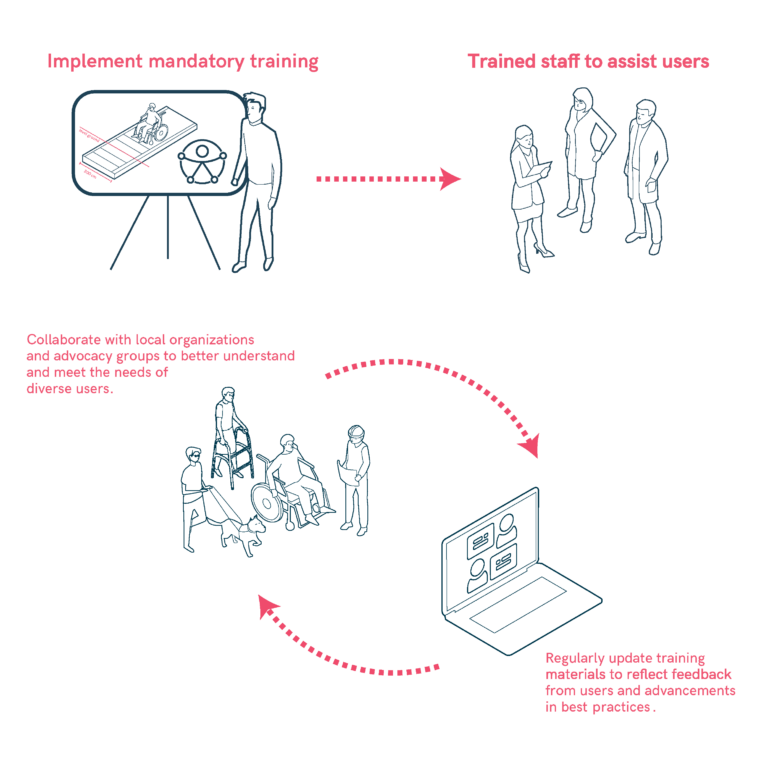
Training and Education